SAN DIEGO, CA – Genes are like instructions, but with options for building more than one thing. Daniel Larson, senior investigator at the National Cancer Institute, studies this gene “splicing” process, which happens in normal cells and goes awry in blood cancers like leukemia. Larson, postdoctoral associate Yihan Wan, and colleagues developed a new technique to study gene splicing at an unprecedented scale, revealing new details into the process. Larson will present the team’s work on Sunday, February 16, at the 64th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society in San Diego, California.
Imagine a long list of instructions with three parts. If you cut and paste sections one and two together you could build a pick-up truck, or if you glued part one and three, you could make a car. Since you wouldn’t want to cut the original template and lose part of your instructions forever, you start by making a copy. This is how it works in our cells—DNA instructions are copied into RNA, before being cut and spliced together, and serving as instructions for a protein and its variations. Gene splicing is an important way that gene expression is regulated to create protein diversity.
“Splicing is one of the long standing mysteries in gene expression, especially for human genes because most of the gene gets cut out. We still don’t know how the cell knows where to splice,” Larson says. “We also have very little idea of how splicing varies from cell to cell and its consequences for biology.” To start answering those questions, Larson, Wan, and colleagues developed and implemented a genetic trick to label thousands of genes at once to generate a comprehensive view of how RNA is being made and processed.
The team inserted a gene into the genome of human cells that causes RNA transcripts to become fluorescent. Using high-throughput single-cell imaging across thousands of cells, they tracked the RNAs from individual genes as they were made and spliced in real-time. Though the fluorescent probe was inserted randomly into the genome, they were able to use deep sequencing to determine which gene had been labeled, and then match that data to the imaging data.
“Our results, from nearly 1,000 genes, show that splicing happens far more often than anyone previously expected,” Larson says. He also revealed that there’s an incredible amount of variability in gene expression timing, from the amount of time a gene stays dormant, to the amount of time before splicing occurs. And the spliceosome, the cellular machine that does the splicing, seems to be very effective at this cutting and pasting process, even when it has huge pieces to remove.
Larson hopes his new method will help scientists fully understand gene splicing by the spliceosome. “Because the spliceosome is frequently mutated in cancer, how the spliceosome is making decisions and what these spliceosomes do is a pressing question in medicine,” Larson says.
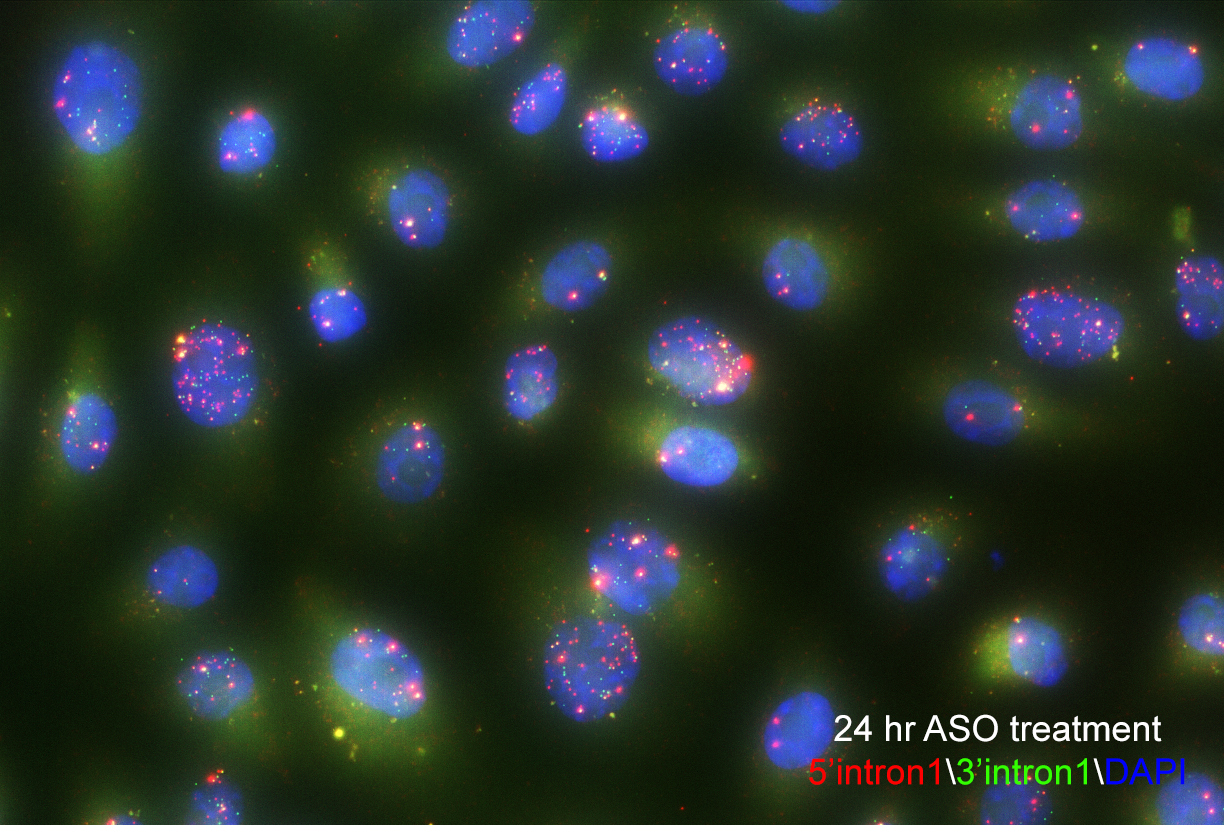
Single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization enables researchers to see splicing intermediates in single cells. Image courtesy of Yihan Wan, PhD.